Blockchain Technology: An Overview
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, also known as distributed ledger technology (DLT), has emerged as a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize various industries. It is a decentralized digital system that allows transactions to be securely recorded and verified across multiple computers or nodes. This technology gained prominence with the invention of Bitcoin, a cryptocurrency that uses blockchain as its underlying technology.
The Basics of Blockchain Technology
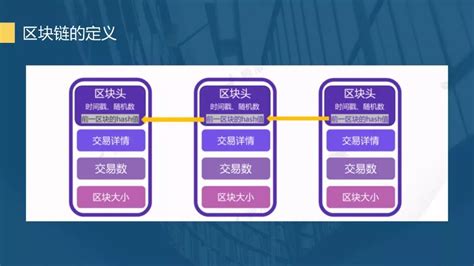
At its core, blockchain technology is a chain of blocks, with each block containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes, forming an immutable and tamperproof record of transactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity has control over the network, making it inherently secure and resistant to censorship.
Key Components of Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peertopeer network, where every participant in the network has a copy of the entire blockchain. This distributed nature eliminates the need for intermediaries and intermediaries, making transactions more efficient and secure.
2. Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain networks employ various consensus mechanisms to validate and agree on the state of the blockchain. Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are the most commonly used consensus mechanisms, ensuring that only valid transactions are added to the blockchain.
3. Cryptography: Blockchain relies heavily on cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions and protect data. Publickey cryptography enables users to have a unique digital identity and to authenticate and encrypt transactions.
Applications and Benefits of Blockchain Technology
1. Financial Services: The most wellknown application of blockchain technology is in the financial industry. Blockchain can facilitate faster, more secure, and transparent transactions, streamlining processes such as crossborder payments, trade finance, and remittances.
2. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology can revolutionize supply chain management by providing endtoend visibility and traceability of products. It enables secure and transparent tracking of goods, reducing fraud, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies in the supply chain.
3. Healthcare: Blockchain has the potential to transform healthcare by enabling secure and interoperable health data exchange. Patients can have control over their medical records, and healthcare providers can securely access and share patient information, improving patient outcomes and reducing medical errors.
4. Identity Management: Blockchain can provide a secure and decentralized identity management system. It enables individuals to maintain control over their digital identities, reducing identity theft and fraud.
5. Voting Systems: Blockchain technology can enhance the integrity and transparency of voting systems. It can ensure that votes are recorded accurately, securely, and anonymously, protecting the democratic process.
Guidelines for Implementing Blockchain Technology
1. Clearly Define the Use Case: Before implementing blockchain technology, it is crucial to identify a specific problem that blockchain can solve. Carefully analyze the benefits and limitations of blockchain in addressing the identified use case.
2. Ensure Scalability and Efficiency: As blockchain technology matures, scalability remains a challenge. Evaluate the scalability and efficiency of different blockchain platforms and architectures to ensure they can handle the desired transaction volume without compromising performance.
3. Collaborate and Build Ecosystems: Blockchain applications often involve multiple parties, requiring collaboration and interoperability. Establish partnerships with relevant stakeholders and build ecosystems to ensure the successful adoption of blockchain technology.
4. Regulatory Compliance: Consider the regulatory environment in which the blockchain application operates. Ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations, especially concerning data privacy and security.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt various industries by providing secure, transparent, and efficient solutions. It is essential to understand the basics of blockchain technology and its key components to explore its potential applications fully. By carefully considering use cases, scalability, collaboration, and regulatory compliance, organizations can harness the power of blockchain to drive innovation and transform their operations.
标签: 区块链术语英文 区块链技术英语怎么说 区块链专业术语英语对照 区块链技术名词中英对照






